

Knowing the electron gain enthalpy values of O—>O– and O—>O2- as -141 and 702 kJ mol-1 respectively, how can you account for the formation of a large number of oxides having O2- species and not O–?
Let us consider the reaction of oxygen with monopositve metal, we can have two compounds. MO(O in -1 state) and M2O (O in -2 state). The energy required for formation of O-2 is compensated by increased coulombic attraction between M+ and O-2. Coulombic force of attraction, FA is proportional to product of charges on ions i.e.
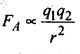
where q1 and q2 are charges on ions and r is distance between ions. Same logic can be applied if metal is dispositive.
Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P4O10. Write the reaction involved. Also write the resonating structures of the oxide of nitrogen formed.
Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H2PO2 (b) H3BO3 (C)H3PO4(d)H3PO3
Which of the following statements are correct for SO2 gas?
(a) It acts as a bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(b) Its molecule has a linear geometry.
(c) Its dilute solution is used as disinfectant.
(d) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute H2SO4 with metal sulphide.
Assertion (A): HI cannot be prepared by the reaction of KI with concentrated H2SO4.
Reason (R): HI has lowest H – X bond strength among halogen acids.
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(b) Leaving F – F bond, all halogens have weaker X – X bond than X – X’ bond in interhalogens.
(c) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms ate present in iodine fluoride.
(d) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
On reaction with Cl2, phosphorus forms two types of halides ‘A' and ‘B'. Halide A is yellowish-white powder but halide B' is colourless oily liquid. Identify A and B and write the formulas of their hydrolysis products.
Name three oxoacids of nitrogen. Write the disproportionation reaction of that oxoacid of nitrogen in which nitrogen is in +3 oxidation state.
Assertion (A): HNO3 makes from passive.
Reason (R): HNO3 forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Assertion (A): NaCl reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to give colourless fumes with pungent smell. But on adding MnO2 the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason (R): MnO2 oxidises HCl to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow.
An amorphous solid "A"bums in air to form a gas "B"which turns lime water milky. The gas is also produced as a by-product during roasting of sulphide ore. This gas decolourises acidified aqueous KMnO4 solution and reduces Fe3+ to Fe+2. Identify the solid "A"and the gas "B"and write the reactions involved.
What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in S02 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal ?
On addition of cone. H2SO4 to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because

On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
(a) It is highly poisonous and has smell like rotten fish.
(b) Its solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(c) It is more basic than NH3
(d) It is less basic than NH3
Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus ? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2009)
With which neutral molecule is ClO– isoelectronic? Is this molecule Lewis acid or base ? (Pb. Board 2009)
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.