

What inspired N. Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6?
N. Bartlett observed that PtF6 reacts with O2to give an compound O2+ [PtF6]–.
PtF6 (g) + O2 (g) ——–>O2+[PtF6]–
Since the first ionization enthalpy of Xe (1170 kJ mol-1 )is fairly close to that of 02 molecule (1175 kJ mol-1 ), he thought that PtF6 should also oxidise Xe to Xe+. This inspired Bartlett to carryout the reaction between Xe and PtF6. When PtF6 and Xe were made to react, a rapid reaction took place and a red solid, Xe+[PtF6]– was obtained.
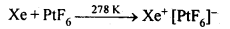
Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus ? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2009)
Knowing the electron gain enthalpy values of O—>O– and O—>O2- as -141 and 702 kJ mol-1 respectively, how can you account for [he formation of a large number of oxides having O2- species and not O–?
Explain why inspite of nearly the same electronegativity, nitrogen forms hydrogen bonding while chlorine does not.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(b) Leaving F – F bond, all halogens have weaker X – X bond than X – X’ bond in interhalogens.
(c) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms ate present in iodine fluoride.
(d) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) All three N – O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(c) P4 molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl5 is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
Assertion (A): SF6 cannot be hydrolysed but SF4 can be.
Reason (R): Six F atoms in SF6 prevent the attack of H2O on sulphur atom of SF6.
On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
(a) It is highly poisonous and has smell like rotten fish.
(b) Its solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(c) It is more basic than NH3
(d) It is less basic than NH3
Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H2PO2 (b) H3BO3 (C)H3PO4(d)H3PO3
Which of the following options are not in accordance with the properly mentioned against them?

Which of the following is correct for P4 molecule of white phosphorus?
(a) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons (b) It has six P – P single bonds
(c) It has three P – P single bonds (d) It has four lone pairs of electrons,
Which of the following statements are correct for SO2 gas?
(a) It acts as a bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(b) Its molecule has a linear geometry.
(c) Its dilute solution is used as disinfectant.
(d) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute H2SO4 with metal sulphide.
Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against each?

Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on cooling is diamagnetic?
In the ring test of NO3 ion.Fe2+ion reduces nitrate ion to nitric oxide, which combines with Fe2+ (aq.) ion to form brown complex. Write the reactions involved in the formation of brown ring.
PCl5 reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH3 solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happens.
What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in S02 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal ?
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
The HNH angle value is higher than HPH, H AsH and HSbH angles. Why?
(Hint: Can be explained on the basis of sp3 hybridisation in NH3 and only s-p bonding , between hydrogen and other elements of the group).