

Discuss the trends in chemical reactivity of group 15 elements.
Hydrides: All elements of group 15 form gaseous hydrides of the type MH3.
In all the hydrides the central atom is sp3 hybridized and their shape is pyramidal due to presence of lone pair of electrons.
(a)The basic strength of the hydrides decreases as we move down the group.
Thus, NH3 is the strongest base.
NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
(b)The thermal stability of the hydrides decreases as the atomic size increases, i.e., the M – H bond strength decreases which means reducing character increases.
(c)In the liquid state, the molecules of NH3are associated due to hydrogen bonding. The molecules of other hydrides are not associated.
(d)NH3 is soluble in water whereas other hydrides are insoluble.
(e)All the hydrides, except NH3, are strong reducing agents and react with metal ions (Ag+, Cu2+, etc.) to form phosphides, arsenides or antimonides.
Halides: The elements of group 15 form two series of halides MX3 and MX5.
(a)All the elements of the group form trihalides. The ionic character of trihalides increases as we move down the group. Except NCl3 all the trihalides are hydrolysed by water. This is due to the absence of d-orbitals in nitrogen.
(b)PF3 is not hydrolysed because fluorine being more electronegative than oxygen forms more stable bonds with phosphorus than P – O bonds.
(c)N cannot form NX5 because of non-availability of rforbitals. Bi cannot form BiX3 because of reluctance of 6s electrons of Bi to participate in bond formation.
(d)The hybridisation of M in MX3 is sp3 and shape is pyramidal. M in MX5 is sp3 as hybridised and shape is trigonal pyramidal. The axial bonds in MX5 are weaker and longer, So MX5 are less stable and decompose on heating eg:
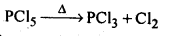
Oxides:
(a)Nitrogen forms a number of oxides. The rest of the members (P, As, Sb and Bi) of the group form two types of oxides : E203 and E2O5.
(b)The reluctance of P, As, Sb and Bi to enter into pπ -pπ multiple bonding leads to cage structures of their oxides and they exist as dimers, E4O6 and E5O10.
(c)The basic nature of die oxides increases with increase in atomic number of the element. Thus, the oxides of nitrogen (except N20 and NO), P (III) and As (III) are acidic, Sb (III) oxide is amphoteric and Bi (III) oxide is basic.
Write balanced equations for the following:
(i) NaCl is heated witlrsulphuric acid in the presence of MnO2
(ii) Chlorine gas is passed into a solution of Nal in water.
Match the formulas of oxides given in Column I with the type of oxide given in Column II and mark the correct option.

How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
If chlorine gas is passed through hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are —— and ——-
Which of the following statements are true?
(a) Only type of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(b) Ionisation enthalpy of.molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(c) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is a redox reaction.
(d) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H2PO2 (b) H3BO3 (C)H3PO4(d)H3PO3
What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus ? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2009)
What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2 ?
What happens when sulp'hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
What are the oxidation states of phosphorus in the following: –
(i) H3PO3 (ii)PCl3
(iii) Ca3P2(iv)Na3PO4
(v) POF3
Which of the following is correct for P4 molecule of white phosphorus?
(a) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons (b) It has six P – P single bonds
(c) It has three P – P single bonds (d) It has four lone pairs of electrons,
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) All three N – O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(c) P4 molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl5 is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
Knowing the electron gain enthalpy values of O—>O– and O—>O2- as -141 and 702 kJ mol-1 respectively, how can you account for the formation of a large number of oxides having O2- species and not O–?
Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 15 elements?
Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in S02 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal ?
In qualitative analysis when H2S is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. HCl, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. HNO3, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives

Which of the following options are not in accordance with the properly mentioned against them?

In PCl5, phosphorus is in sp3d hybridised state but all its five bonds are not equivalent. Justify your answer with reason.
Assertion (A): Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur exist as S8 but oxygen exists as OÏ€.
Reason (R): Oxygen forms pπ-pπ multiple bond due to small size and small bond length but pπ-pπ bonding is not possible in sulphur.
Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising powers of F2 and Cl2.