

Discuss the trends in chemical reactivity of group 15 elements.
Hydrides: All elements of group 15 form gaseous hydrides of the type MH3.
In all the hydrides the central atom is sp3 hybridized and their shape is pyramidal due to presence of lone pair of electrons.
(a)The basic strength of the hydrides decreases as we move down the group.
Thus, NH3 is the strongest base.
NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
(b)The thermal stability of the hydrides decreases as the atomic size increases, i.e., the M – H bond strength decreases which means reducing character increases.
(c)In the liquid state, the molecules of NH3are associated due to hydrogen bonding. The molecules of other hydrides are not associated.
(d)NH3 is soluble in water whereas other hydrides are insoluble.
(e)All the hydrides, except NH3, are strong reducing agents and react with metal ions (Ag+, Cu2+, etc.) to form phosphides, arsenides or antimonides.
Halides: The elements of group 15 form two series of halides MX3 and MX5.
(a)All the elements of the group form trihalides. The ionic character of trihalides increases as we move down the group. Except NCl3 all the trihalides are hydrolysed by water. This is due to the absence of d-orbitals in nitrogen.
(b)PF3 is not hydrolysed because fluorine being more electronegative than oxygen forms more stable bonds with phosphorus than P – O bonds.
(c)N cannot form NX5 because of non-availability of rforbitals. Bi cannot form BiX3 because of reluctance of 6s electrons of Bi to participate in bond formation.
(d)The hybridisation of M in MX3 is sp3 and shape is pyramidal. M in MX5 is sp3 as hybridised and shape is trigonal pyramidal. The axial bonds in MX5 are weaker and longer, So MX5 are less stable and decompose on heating eg:
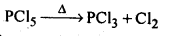
Oxides:
(a)Nitrogen forms a number of oxides. The rest of the members (P, As, Sb and Bi) of the group form two types of oxides : E203 and E2O5.
(b)The reluctance of P, As, Sb and Bi to enter into pπ -pπ multiple bonding leads to cage structures of their oxides and they exist as dimers, E4O6 and E5O10.
(c)The basic nature of die oxides increases with increase in atomic number of the element. Thus, the oxides of nitrogen (except N20 and NO), P (III) and As (III) are acidic, Sb (III) oxide is amphoteric and Bi (III) oxide is basic.
With which neutral molecule is ClO– isoelectronic? Is this molecule Lewis acid or base ? (Pb. Board 2009)
Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H2PO2 (b) H3BO3 (C)H3PO4(d)H3PO3
Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus ? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2009)
On heating ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately we get
(a) N2 in both cases
(b) N2 with ammonium dichromate and NO with barium azide
(c) N2O with ammonium dichromate and N2 with barium azide
(d) N2O with ammonium dichromate and N2O with barium azide
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(b) Leaving F – F bond, all halogens have weaker X – X bond than X – X’ bond in interhalogens.
(c) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms ate present in iodine fluoride.
(d) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids. Out of these oxoacids phosphinic acid has strong reducing property. Write its structure and also write a reaction showing its reducing behaviour.
Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P4O10. Write the reaction involved. Also write the resonating structures of the oxide of nitrogen formed.
Assertion (A): HI cannot be prepared by the reaction of KI with concentrated H2SO4.
Reason (R): HI has lowest H – X bond strength among halogen acids.
Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 15 elements? (C.B.S.E. 2013)
What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in S02 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal ?
Write balanced equations for the following:
(i) NaCl is heated witlrsulphuric acid in the presence of MnO2
(ii) Chlorine gas is passed into a solution of Nal in water.
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) All three N – O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(c) P4 molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl5 is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
Write a balanced chemical equation, for the reaction showing catalytic oxidation of NH3 by atmospheric oxygen.
Explain why does the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increase in the order given below:
HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
P4O6 reacts with water according to equation P4O6 + 6H2O Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralize the acid formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P4O6 in H2O.
Assertion (A): HNO3 makes from passive.
Reason (R): HNO3 forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Explain why inspite of nearly the same electronegativity, nitrogen forms hydrogen bonding while chlorine does not.
Discuss the general characteristics of Group 15 elements with reference to their electronic configuration, oxidation state, atomic size, ionisation enthalpy and electronegativity.
The HNH angle value is higher than HPH, H AsH and HSbH angles. Why?
(Hint: Can be explained on the basis of sp3 hybridisation in NH3 and only s-p bonding , between hydrogen and other elements of the group).