

Why does O3 act as a powerful oxidising agent?
On heating, O3 readily decomposes to give O2 and nascent oxygen.
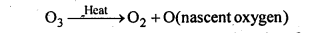
Since nascent oxygen is very reactive, therefore, O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Write balanced equations for the following:
(i) NaCl is heated witlrsulphuric acid in the presence of MnO2
(ii) Chlorine gas is passed into a solution of Nal in water.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) All three N – O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(c) P4 molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl5 is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
Which of the following statements are true?
(a) Only type of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(b) Ionisation enthalpy of.molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(c) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is a redox reaction.
(d) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus ? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2009)
What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2 ?
Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H2PO2 (b) H3BO3 (C)H3PO4(d)H3PO3
Match the formulas of oxides given in Column I with the type of oxide given in Column II and mark the correct option.

Arrange the following in the order of property indicated for each set: –
(i) F2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2 – increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii) HF, HCI, HBr, HI – increasing acid . strength.
(iii) NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 – increasing Sol. base strength.
How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions . involved.
In qualitative analysis when H2S is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. HCl, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. HNO3, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives

If chlorine gas is passed through hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are —— and ——-
Which of the following is correct for P4 molecule of white phosphorus?
(a) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons (b) It has six P – P single bonds
(c) It has three P – P single bonds (d) It has four lone pairs of electrons,
Assertion (A): HNO3 makes from passive.
Reason (R): HNO3 forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
With which neutral molecule is ClO– isoelectronic? Is this molecule Lewis acid or base ? (Pb. Board 2009)
The HNH angle value is higher than HPH, H AsH and HSbH angles. Why?
(Hint: Can be explained on the basis of sp3 hybridisation in NH3 and only s-p bonding , between hydrogen and other elements of the group).
What are the oxidation states of phosphorus in the following: –
(i) H3PO3 (ii)PCl3
(iii) Ca3P2(iv)Na3PO4
(v) POF3
Phosphorus has three allotropic fonns —(i) white phosphorus (ii) red phosphorus and (iii) black phosphorus. Write the difference between white and red phosphorus on the basis of their structure and reactivity.
Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising powers of F2 and Cl2.