

Give reasons for the following: ‘
(a) Covalent bonds are directional bonds while ionic bonds are non- directional.
(b) Water molecule has bent structure whereas carbon dioxide molecule is linear.
(c) Ethyne molecule is linear.
(i) Since the covalent bond depends on the overlapping of orbitals between different orbitals, the geometry of the molecule is different. The orientation of overlap is different. The orientation of overlap is the factor responsible for their directional nature.
(ii) Due to presence of two lone pairs of electrons on oxygen atom in HiO the repulsion between Ip-lp is more. C02 undergoes sp hybridization resulting in linear shape (O = C = O) while H20 undergoes .sp3 hybridisation resulting in distorted tetrahedral or bent structure.

(iii) In ethyne molecule carbon undergoes sp hybridization with two unhybridised orbitals. One sp hybrid orbital of one carbon atom overlaps axially with sp hybrid orbital of the other carbon atom to form C – C sigma bond while the other hybridized orbital of each carbon atom overlaps axially with S orbitals of hydrogen atoms forming σ bonds. Unhybridised orbitals form Ï€ bonds

Match the species in Column I with the geometry/shape in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) H30+ | (a) Linear |
| (ii) HC = CH | (b) Angular |
| (iii) Cl0–2 | (c) Tetrahedral |
| (iv) NH+4 | (d) Trigonal bipyramidal |
| – | (e) Pyramidal |
Which of the following statements are correct about CO32- ?
(a) The hybridization of central atom is sp3.
(b) Its resonance structure has one C – O single bond and two C = O double bonds.
(c) The average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units.
(d) All C – O bond lengths are equal.
Account for the following:
(i) Water is a liquid while H2S is a gas
(ii) NH3 has higher boiling point than PH3.
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
(a) HCl
(b) H20
(c) HI
(d) H2S
Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic character of 0+2 and O–2
Name the two conditions which must be satisfied for hydrogen bonding to take place in a molecule.
Match the shape of molecules in Column I with the type of hybridization in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Tetrahedral | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Trigonal | (b) sp |
| (iii) Linear | (c) sp3 |
The skeletal structure of CH3COOH as shown below is correct, but some of the bonds are shown incorrectly. Write the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid.
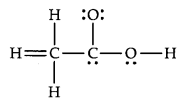
Draw diagrams showing the formation of a double bond and a triple bond between carbon atoms in C2 H4 and C2 H2 molecules.
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
(a) CH3-CH3 (b) CH3-CH = CH2 (c) CH3-CH2-OH (d) CH3-CHO (e) CH3COOH.
What is meant by the term average bond enthalpy? Why there is difference in bond enthalpy of O – H bond in ethanol (C2H5OH) and water?
3PO3 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing H3PO3? If not, give reasons for the same.
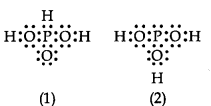
What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals? Describe the shapes of sp, sp2, sp3 hybrid orbitals.
(a) How many a and n bonds are present in
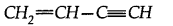
(b) Why Hf is more stable than H2?
(c) Why is B2 molecule paramagnetic?
In N0–3 ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atom are
(a) 2, 2 (b) 3, 1 (c) 1,3 (d) 4, 0
Arrange the following bonds ‘in order of increasing ionic character giving reason.
N-H, F-H, C-H and O-H
Predict the shapes of the following molecules on the basis of hybridization. BC13, ch4, co2, nh3
Assertion (A): Though the central atom of both NH3 and H20 molecules are sp3 hybridised, yet H – N – H bond angle is greater than that of H – O – H.
Reason (R): This is because nitrogen atom has one lone pair and oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
(a) A and R both are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A and R both are false.
Discuss the shape of the following molecules using the VSEPR model:
BeCl2, BCl3 , SiCl4, AsF5, H2S, PH3
Define Lattice energy. How is Lattice energy influenced by (i) Charge on the ions (ii) Size of the ions?
Explain the diamagnetic behaviour of P2 molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory.
Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the comers of the square and the C atoms at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar?
In which of the following molecule/ion all the bonds are not equal?
(a) XeF4
(b) BF–4
(c) C2H4
(d) SiF4
Explain the non linear shape of H2S and non planar shape of PCl3 using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
The energy of σ2pz: molecular orbital is greater than 2px and 2pv molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule. Write the complete sequence of energy levels in the increasing order of energy in the molecule. Compare the relative stability and the magnetic behaviour of the following species:
N2, N+2, N–2, N22+
What is an ionic bond? With two suitable examples explain the difference between an ionic and covalent bond?
Match the species in Column I with the bond order in Column II.
| Column I | , . Column II |
| (i) NO | (a) 1.5 |
| (ii) CO | (b) 2.0 |
| (iii) o–2 | (c) 2.5 |
| (iv) 02 | (d) 3.0 |