

Write the type of hybridisation involved in CH4,C2H4 and C2H2.
CH4= sp3
C2H4 = sp2
C2H2 = sp
Elements X, Y and Z have 4, 5 and 7 valence electrons respectively, (i) Write the molecular formula of the compounds formed by these elements individually with hydrogen, (ii) Which of these compounds will have the highest dipole moment?
Assertion (A): Though the central atom of both NH3 and H20 molecules are sp3 hybridised, yet H – N – H bond angle is greater than that of H – O – H.
Reason (R): This is because nitrogen atom has one lone pair and oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
(a) A and R both are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A and R both are false.
Which of the following statements are not correct?
(a) NaCl being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the solid state.
(b) In canonical structures there is a difference in the arrangement of atoms.
(c) Hybrid orbitals form stronger bonds than pure orbitals.
(d) VSEPR theory can explain the square planar geometry of XeF4.
The skeletal structure of CH3COOH as shown below is correct, but some of the bonds are shown incorrectly. Write the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid.
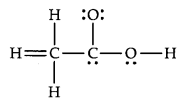
Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in the bond formation?

Arrange the following bonds ‘in order of increasing ionic character giving reason.
N-H, F-H, C-H and O-H
Although both CO2 and H2O are triatomic molecules, the shape of H2O molecule is bent while that of CO2 is linear. Explain this on the basis of dipole moment.
Name the two conditions which must be satisfied for hydrogen bonding to take place in a molecule.
Is there any change in the hybridisation ofB and N atoms as a result of the following reaction ? BF3 + NH3 ——-> F3 B.NH3
Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic character of 0+2 and O–2
Assertion (A): Among the two O – H bonds in H20 molecule, the energy required to break the first O – H bond and other O – H bond is the same.
Reason (R): This is because the electronic environment around oxygen is the same even after breakage of one O – H bond.
(a) A and R both are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A and R both are false.
Write the important conditions required for the linear combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals.
Account for the following:
(i) Water is a liquid while H2S is a gas
(ii) NH3 has higher boiling point than PH3.
What is meant by the term average bond enthalpy? Why there is difference in bond enthalpy of O – H bond in ethanol (C2H5OH) and water?
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
(a) C2 H2 (b) C2 H4
(a) How many a and n bonds are present in
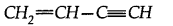
(b) Why Hf is more stable than H2?
(c) Why is B2 molecule paramagnetic?
Structures of molecules of two compounds are given below:

(a) Which of the two compounds will have intermolccular hydrogen bonding and which compound is expected to show intramolecular hydrogen bonding?
(b) The melting point of a compound depends on. among other things, the extent of hydrogen bonding. On this basis explain which of the above two compounds will show higher melting point.
(c) Solubility of compounds in water depends on power to form hydrogen bonds with water. Which of the above compounds will form hydrogen bond with water easily and be more soluble in it?
Match the species in Column I with the type of hybrid orbitals in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) SF4 | (a) sp3cf |
| (ii) if5 | (b) d2sp3 |
| (iii) NO2+ | (c) sp3 d |
| (iv) NH4 | (d) sp3 |
| (e) sp |
Match the items given in Column I with examples given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Hydrogen bond | (a) C |
| (ii) Resonance | (b) LiF |
| (iii) Ionic solid | (c) H2 |
| (iv) Covalent solid | (d) HF |
| (e) 03 |
Explain why BeH2 molecule has a zero dipole moment although the Be—H bonds are polar.
What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illustrate by giving one example of each type.
Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the comers of the square and the C atoms at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar?
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
(a) C02
(b) HI
(c) H20
(d) S02
In N0–3 ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atom are
(a) 2, 2 (b) 3, 1 (c) 1,3 (d) 4, 0
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
(a) HCl
(b) H20
(c) HI
(d) H2S
What is the effect of the following processes on the bond order in N-, and 02?
(i) N2 → N+2 + e– (ii) 02 → O+2 + e–
What is an ionic bond? With two suitable examples explain the difference between an ionic and covalent bond?
Explain why CO2-3 ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure. How can it be best represented?
Match the shape of molecules in Column I with the type of hybridization in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Tetrahedral | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Trigonal | (b) sp |
| (iii) Linear | (c) sp3 |