



Explain why pure liquids and solids can be ignored while writing the value of equilibrium constants.
The pH of a sample of vinegar is 3.76. Calculate the concentration of hydrogen ion in it.
Conjugate acid of a weak base is always stronger. What will be the decreasing order of basic strength of the following conjugate bases?
OH–, RO–, ch3coo– , cl–
Does the number of moles of reaction products increase, decrease or remain same when each of the following equilibria is subjected to a decrease in pressure bp increasing the volume?
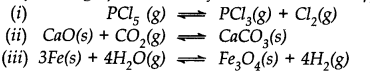
Hydrogen gas is obtained from the natural gas by partial oxidation with steam as per following endothermic reaction:

Write the expression for Kpfor the above reaction
How will the value of Kp and composition of equilibrium mixture be affected by:
(i) increasing the pressure, (ii) increasing the temperature, (iii) using a catalyst?
What is meant by conjugate acid-base pair? Find the conjugate acid/base for the following species: HNO2, CH–, HClO4 , OH–, CO32-, S2-
Calculate (a) ∆G– and (b) the equilibrium constant for the formation of N02 from NO and 02 at 298 K
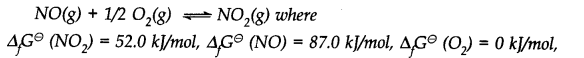
Which of the following reactions will get affected by increase in pressure ? Also mention whether the change will cause the reaction to go to the right or left direction.
Match the following equilibria with the corresponding condition
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Liquid⇌Vapour | (a) | Saturated solution |
| (ii) | Solid ⇌Liquid | (b) | Boiling point |
| (iii) | Solid ⇌Vapour | (c) | Sublimation point |
| (iv) | Solute(s) ⇌Solute (solution) | (d) | Melting point ‘ |
| (e) | Unsaturated solution | ||
The concentration of hydrogen ions in a sample of soft drink is 3.8 x 10-3 M. What is the pH value?
The ionization constant of an acid, Ka is the measure of strength of an acid. The Ka values of acetic acid, hypochlorous acid and formic acid are 1.74 x 10-5, 3.0 x 10-8 and 1.8 x 10-4 Which of the following orders of pH of 0.1 mol dm-3 solutions of these acids is correct?
(a) acetic acid > hypochlorous acid > formic acid
(b) hypochlorous acid > acetic acid > formic acid
(c) formic acid > hypochlorous acid > acetic acid
(d) formic acid > acetic acid > hypochlorous acid
At a particular temperature and atmospheric pressure, the solid and liquid phases of a pure substance can exist in equilibrium. Which of the following term defines this temperature? .
(a) Normal melting point
(b) Equilibrium temperature
(c) Boiling point
(d) Freezing point
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron
(II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and C02
FeO(s) + CO(g) ———>Fe(s) + C02(g) ; Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 K
What are the equilibrium partial pressures of CO and C02 at 1050 K if the initial pressures are: PCO = 1.4 atm and PCO2 = 0.80 atm?
The ionization constant of phenol is 1.0 x 10-10. What is the concentration of phenolate ion in 0.05 M solution of phenol? What will be its degree of ionization if the solution is also 0.01 M in sodium phenolate?
The ionization constant of acetic acid is 1.74 x 10-5. Calculate the degree of dissociation of acetic acid in its 0.05 M solution. Calculate the concentration of acetate ions in the solution and its pH.
Ionization constant of a weak base MOH, is given by the expression

Values of ionization constant of some weak bases at a particular temperature are given below:
| Base | Dimethylamine | Urea | Pyridine | Ammonia |
| 5.4 x 10-4 | 1.3 x 10-14 | 1.77 x lO-9 | 1.77 xlO-5 |
Arrange the bases in decreasing order of the extent of their ionization at equilibrium. Which of the above base is the strongest?
The value of Kc for the reaction
2HI(g) ⇌H2(g) + I2(g) is 1 x 10-4. At a given time, the composition of reaction mixture is [HI] = 2 x 10-5 mol, [H2] = 1 x 10-5 mol and [I2] = 1 x 10-5 mol. In which direction will the reaction proceed?
Calculate the pH of a solution formed by mixing equal volumes of two solutions A and B of a strong acid having pH = 6 and pH = 4 respectively.
The solubility product of Al(OH)3 is 2.7 x 10-11. Calculate its solubility in g–L and also find out pH of this solution. (Atomic mass of A1 = 27 u).
Bromine monochloride (BrCl ) decomposes into bromine and chlorine and reaches the equilibrium:
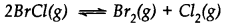
The value of Kc is 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3.3 x10-3mol L-1what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
At 473 K, the equilibrium constant Kc for the decomposition of phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is 8.3 x 10-3 . if decomposition proceeds as:
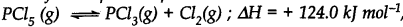
(a) Write an expression for Kc for the reaction
(b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at the same temperature.
(c) What would be the effect on Kc if
(i) More of PCl5is added (ii) Temperature is increased.
The pH of0.005 M codeine (C18H21N03) solution is 9.95. Calculate the ionization constant and PKb.
(i) Define Le Chatelier’s principle.
(ii) Following reactions occur in a Blast furnace.
Fe203(s) + 3CO(g) ———–>2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
use Le chatelier’s principle to predict the direction of reaction when equilibrium mixture is disturbed by
(a) adding Fe203 (b) removing CO2 .
(c) removing CO.
PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2 are at equilibrium at 500 K and having concentration 1.59M PCl5 1.59M Cl2 and 1.41M PCl5. Calculate Kc for the reaction PCl5———>PC13+ Cl2
The ionization of hydrochloric acid in water is given below:
HCl(aq) + H20(l) ⇌H30 + (aq) +Cl–(aq)
Label two conjugate acid-base pairs in this ionization.
On the basis of the equation pH = -log [H+], the pH of 10-8 mol dm-3 solution of HC1 should be 8. However, it is observed to be less than 7.0. Explain the reason.
pH of a solution of a strong acid is 5.0. What will be the pH of the solution obtained after diluting the given solution a 100 times?
A mixture of 1.57 mol of N2, 1.92 mol of H2 and 8.13 mol of NH3is introduced into a 20 L reaction vessel at 500 K. At this temperature, the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction
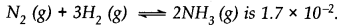
Is this reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the direction of net reaction?
Classify the following species into Lewis acids and Lewis bases and show how these can act as Lewis acid/Lewis base?
(a) OH– ions (b) F– (c) H+ (d) BCl3
The ionization constant of HF, HCOOH and HCN at 298 K are is 6.8 x 10-4 , 1.8 x 10-4 and 4.8 x 10-9 respectively, Calculate the ionization constant of the corresponding conjugate base.
It has been found that the pH of a 0.01 M solution of an organic acid is 4.15. Calculate the concentration of the anion, the ionization constant of the acid and its PKa.