

Define solubility product.
It is product of molar concentration of ion raised to the power of number of ions produced per compound in saturated solution.
The value of Kc for the reaction 302(g) —>203(g) is 2.0 x 10-50 at 25 °C. If equilibrium concentration of 02 in air at 25 °C is 1.6 x 10-2, what is the concentration of O3?
For the reaction N204(g) ⇌2N02(g), the value of K is 50 at 400 K and 1700 at 500 K. Which of the following options is correct?
(a) The reaction is endothermic.
(b) The reaction is exothermic.
(c) If NO2(g) and N204(g) are mixed 400 K at partial pressures 20 bar and 2 bar respectively, more N204(g) will be formed.
(d) The entropy of the system increases.
Arrange the following in increasing order of pH.
KN03(aq), CH3COONa(aq), NH4Cl(aq), C6H5COONH4(aq)
pH of a solution of a strong acid is 5.0. What will be the pH of the solution obtained after diluting the given solution a 100 times?
A sample of HI (g) is placed in a flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equilibrium partial pressure of HI (g) is 0.04 atm. What is Kp for the given equilibrium?
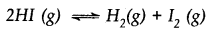
The degree of ionization of a 0.1 M bromoacetic acid solution is 0.132. Calculate the pH of the solution and the PKa of bromoacetic acid.
(i) Define Le Chatelier’s principle.
(ii) Following reactions occur in a Blast furnace.
Fe203(s) + 3CO(g) ———–>2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
use Le chatelier’s principle to predict the direction of reaction when equilibrium mixture is disturbed by
(a) adding Fe203 (b) removing CO2 .
(c) removing CO.
The value of Kc for the reaction 2A——>B + C is 2 x 10-3. At a given time, the composition of reaction mixture is [A] = [B] = [C] = 3 x 10-4 M. In which direction the reaction will proceed?
On the basis of the equation pH = -log [H+], the pH of 10-8 mol dm-3 solution of HC1 should be 8. However, it is observed to be less than 7.0. Explain the reason.
Predict which of the following will have appreciable concentration of reactants and products:
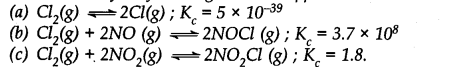
The pH of a sample of vinegar is 3.76. Calculate the concentration of hydrogen ion in it.
The pH of0.005 M codeine (C18H21N03) solution is 9.95. Calculate the ionization constant and PKb.
Hydrogen gas is obtained from the natural gas by partial oxidation with steam as per following endothermic reaction:

Write the expression for Kpfor the above reaction
How will the value of Kp and composition of equilibrium mixture be affected by:
(i) increasing the pressure, (ii) increasing the temperature, (iii) using a catalyst?
The ionization constant of HF, HCOOH and HCN at 298 K are is 6.8 x 10-4 , 1.8 x 10-4 and 4.8 x 10-9 respectively, Calculate the ionization constant of the corresponding conjugate base.
The solubility product of Al(OH)3 is 2.7 x 10-11. Calculate its solubility in g–L and also find out pH of this solution. (Atomic mass of A1 = 27 u).
Dihydrogen gas is obtained from natural gas by partial oxidation with steam as per following endothermic reaction:
CH4(g) + H2O(g) ——> CO(g) + 3 H2(g)
(a) Write an expression for Kpfor the above reaction.
(b) How will the values of Kp and composition of equilibrium mixture be affected by (i) increasing the pressure (ii) increasing the temperature (iii) using a catalyst?
BF3 does not have proton but still acts as an acid and reacts with NH3. Why is it so? What type of bond is formed between the two?
What is meant by conjugate acid-base pair? Find the conjugate acid/base for the following species: HNO2, CH–, HClO4 , OH–, CO32-, S2-
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapours in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. The volume of the container is suddenly increased, (i) What is the initial effect of the change on the vapour pressure? (ii) How do the rates of evaporation and condensation change initially? (iii) What happens when equilibrium is restored finally and what will be the final vapour pressure?
Nitric oxide reacts with bromine and gives nitrosyl bromide as per reaction given below:
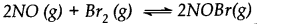
When 0.087 mole of NO and 0.0437 mole of Br2 are mixed in a closed container at constant temperature, 0.0518 mole of NOBr is obtained at equilibrium. Determine the compositions of the equilibrium mixture.
Assuming complete dissociation, calculate the pH of the following solutions:
(a) 0.003 M HCl (b) 0.005 M NaOH (c) 0.002 M HBr (d) 0.002 M KOH
At 473 K, the equilibrium constant Kc for the decomposition of phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is 8.3 x 10-3 . if decomposition proceeds as:
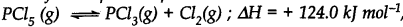
(a) Write an expression for Kc for the reaction
(b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at the same temperature.
(c) What would be the effect on Kc if
(i) More of PCl5is added (ii) Temperature is increased.
PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2 are at equilibrium at 500 K and having concentration 1.59M PCl5 1.59M Cl2 and 1.41M PCl5. Calculate Kc for the reaction PCl5———>PC13+ Cl2
A sparingly soluble salt gets precipitated only when the product of concentration of its ions in the solution (Qsp) becomes greater than its solubility product. If the solubility of BaS04 in water is 8 x 10-4 mol dm-3, calculate its solubility in 0.01 mol dm-3 of H2S04.
Dihydrogen gas used in Haber’s process is produced by reacting methane from natural gas with high temperature steam. The first stage of two stage reaction involves the formation of CO and H2 In second stage, CO formed in first stage is reacted with more steam in water gas shift reaction.

If a reaction vessel at 400 °C is charged with an equimolar mixture of CO and steam so that PCO = PH2O = 4.0 bar, what will be the partial pressure of H2 at equilibrium? Kp = 0.1 at 400 °C.
The concentration of hydrogen ions in a sample of soft drink is 3.8 x 10-3 M. What is the pH value?
Explain why pure liquids and solids can be ignored while writing the value of equilibrium constants.
Which of the following reactions will get affected by increase in pressure ? Also mention whether the change will cause the reaction to go to the right or left direction.
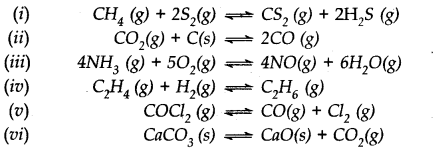
The values of Ksp of two sparingly soluble salts Ni(OH)2 and AgCN are 2.0 x 10-15 and 6 x 10-17 respectively. Which salt is more soluble? Explain.
(i) Point out the differences between ionic product and solubility product.
(ii) The solubility of AgCl in water at 298 K is 1.06 x 10-5 mole per litre. Calculate its solubility product at this temperature.
For the equilibrium 2 NOCl(g)——-> 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) the value of the equilibrium constant Kc is 3.75 x 10-6 at 1069 K. Calculate the Kp for the reaction at this temperature?
The equilibrium constant expression for a gas reaction is,
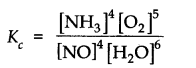
Write the balanced chemical equation corresponding to this expression.
Does the number of moles of reaction products increase, decrease or remain same when each of the following equilibria is subjected to a decrease in pressure bp increasing the volume?
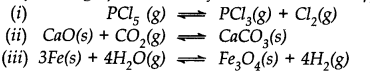
The species H20, HCO3–, HSO4– and NH3 can act both as Bronsted acid and base. For each case, give the corresponding conjugate acid and base.
The ionization constant of phenol is 1.0 x 10-10. What is the concentration of phenolate ion in 0.05 M solution of phenol? What will be its degree of ionization if the solution is also 0.01 M in sodium phenolate?