

Given a uniform electric field E→ = 2 × 103 i^ N/ C, find the flux of this field through a square of side 20 cm, whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square, if the plane makes an angle of 30° with the x-axis? (Delhi 2014)
Given : E→=5×103i^N/C
A = 10 × 10 × 10-4m2,
Flux (Ï•) = EA cos θ
(i) For first case, θ = 0, cos 0 = 1
∴ Flux = (5 × 103) × (10 × 10 × 10-4)
(ii) Angle of square plane with x-axis = 30°
Hence the 0 will be 90° – 30° = 60°
EA cos θ = (5 × 103) × (10 × 10 × 10-4) × cos 60
= 50 × 12
= 25 Nm2C-1
Hint : (i) 80 Nm2C-1
(ii) 40 Nm2C3
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm which encloses an electric dipole? (Delhi 2015)
Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid? Give reason for your answer. (Delhi 2017)
Name the physical quantity whose S.I. unit is JC-1. Is it a scalar or a vector quantity? (All India 2010)
Why are electric field lines perpendicular at a point on an equipotential surface of a conductor? (Comptt. All India 2015)
Show that the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is given by E→=σε0n^, where σ is the surface charge density and h is a unit vector normal to the surface in the outward direction. (All India 201
State Gauss’s law.
A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire of linear charge density ‘X’ is enclosed by a cy¬lindrical surface of radius V and length ‘l’—its axis coinciding with the length of the wire. Obtain the expression for the electric field, indi¬cating its direction, at a point on the surface of the cylinder. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
State Gauss’ law in electrostatics. Using this law derive an expression for the electric field due to a uniformly changed infinite plane sheet.
(i) Use Gauss’s law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
(ii) Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and series combination of two capacitors Cj and C2 with their capacitances in the ratio 1 : 2 so that the energy stored in the two cases becomes the same. (All India 2016)
A point charge +q is placed at a distance d from an isolated conducting plane. The field at a point P on the other side of the plane is
(a) directed perpendicular to the plane and away from the plane
(b) directed perpendicular to the plane but towards the plane
(c) directed radially away from the point charge
(d) directed radially towards the point charge
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus, there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
How does the electric flux due to a point charge enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface get affected when its radius is increased? (Delhi 2016)
Draw a plot showing variation of electric field with distance from the centre of a solid conducting sphere of radius R, having a charge of +Q on its surface. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
(a) Define electric flux. Write its SI units.
(b) The electric field components due to a charge inside the cube of side 0.1 m are as shown :
Ex = ax, where α = 500 N/C-m
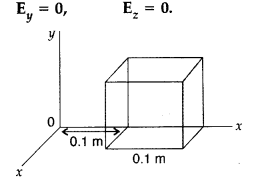
Calculate
(i) the flux through the cube, and
(ii) the charge inside the cube. (All India 2008)
If Фs E . dS = 0 over a surface, then
(a) the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero
(b) the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform
(c) the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it
(d) all charges must necessarily be outside the surface
Two charges of magnitudes – 2Q and + Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a,0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin? (All India 2013)
A positive point charge (+ q) is kept in the vicinity of an uncharged conducting plate. Sketch electric field lines originating from the point on to the surface of the plate.
Derive the expression for the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor. (All India) Answer: Representation of electric field, (due to a positive charge)
Figure shows electric field lines in which an electric dipole P is placed as shown. Which of the following statements is correct?

(a) The dipole will not experience any force
(b)The dipole will experience a force towards right
(c)The dipole will experience a force towards left
(d)The dipole will experience a force upwards
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube? (All India 2012)
Is the electric field due to a charge configuration with total charge zero, necessarily zero? Justify. (Comptt. All India 2012)
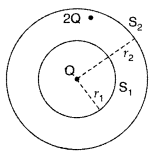
A sphere S1 of radius r1 encloses a net charge Q. If there is another concentric sphere S2 of radius r2 (r2 > r,) enclosing charge 2Q, find the ratio of the electric flux through S1 and S2. How will the electric flux through sphere S1 change if a medium of dielectric constant K is introduced in the space inside S2 in place of air? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Define the term ‘electric flux’. Write its S.I. units. What is the flux due to electric field E→=3×103i^ N/C through a square of side 10 cm, when it is held normal to if? (Comptt. All India 2015)
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atohis, represented by open circles are situated at the comers of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at
the centre of the Cube.

The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
(i) What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
(ii) Suppose that the Cs atom at the comer A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
Two charges q and -3q are placed fixed on x-axis separated by a distance d. Where should a third charge 2q be placed such that it will not experience any force?
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through two opposite faces of the cube? (All India)
What is the direction of the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor having charge density σ < 0? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire having charge density X is enclosed by a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l, its axis coinciding with the length of the wire. Find the expression for the electric flux through the surface of the cylinder. (All India 2011)
Plot a graph showing the variation of coulomb force (F) versus (1r2), where r is the distance between the two charges of each pair of charges : (1µC, 2µC) and (2µC, – 3µC). Interpret the graphs obtained. (All India 2010)
(a) Using Gauss’ law, derive an expression for the electric field intensity at any point outside a uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R and charge density a C/m2. Draw the field lines when the charge density of the sphere is
(i) positive,
(ii) negative.
(b) A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.5 m in diameter has a surface charge density of 100 µC/m2. Calculate the
(i) charge on the sphere
(ii) total electric flux passing through the sphere (Delhi 2008)
A point charge +Q is placed in the vicinity of a conducting surface. Draw the electric field lines between the surface and the charge.
(Comptt. Outside Delhi 2017)
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (a and P), each of surface area .S' are charged to -Q and q, respectively, where Q > q >0. A third identical plate (j), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate p. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst p and y
(a) Find the electric field acting on the plate y before collision.
(b) Find the charges on P and yafter the collision.
(c) Find the velocity of the plate yafter the collision and at a distance d from the plate /?.

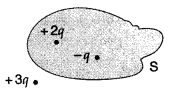
Figure shows three point charges, +2q, -q and + 3q. Two charges +2q and -q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’ (Delhi 2010)
Why must electrostatic field be normal to the surface at every point of a charged conductor? (Delhi 2012)
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field E→ with its dipole moment p⃗ parallel to the field. Find
(i) the work done in turning the dipole till its dipole moment points in the direction
opposite to E→ .
(ii) the orientation of the dipole for which the torque acting on it becomes maximum. (Comptt. All India 2014)
The electric field at a point is
(a) always continuous
(b) continuous if there is no charge at that point
(c) discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point
(d) discontinuous if there is a charge at that point
A paisa coin is made up of Al-Mg alloy and weight 0.75 g. It has a square shape and its diagonal measures 17 mm. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
Figure shows the electric field lines around three point charges A, B and C.

(i) Which charges are positive?
(ii) Which charge has the largest magnitude? Why?
(iii) In which region or regions of the picture could the electric field be zero? Justify your answer.
(a) Near A (b) Near B
(c) Near C (d) Nowhere
In which orientation, a dipole placed in a uniform electric field is in
Define electric flux. Write its S.I. unit.
A charge q is enclosed by a spherical surface of radius R. If the radius is reduced to half, how would the electric flux through the surface change? (All India 2009)
A spherical conducting shell of inner radius rx and outer radius r2 has a charge ‘Q’. A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of the shell.
(a) What is the surface charge density on the
(i) inner surface,
(ii) outer surface of the shell?
(b) Write the expression for the electric field at a point x > r2 from the centre of the shell. (All India 2010)
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
Draw a graph of electric field E(r) with distance r from the centre of the shell for 0 ≤ r ≤ ∞
Use Gauss’s law to derive the expression for the electric field between two uniformly charged large parallel sheets with surface charge densities a and -a respectively. (All India)
(a) Define electric flux. Write its S.I. units.
(b) Using Gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
(c) How is the field directed if
(i) the sheet is positively charged,
(ii) negatively charged? (Delhi 2012)
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the +x-direction on a charge q1, fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1

(a) shall increase along the positive x-axis
(b) shall decrease along the positive x-axis
(c) shall point along the negative x-axis
(d) shall increase but the direction changes because of the intersection of Q with q2 and q3
A metallic spherical shell has an inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A charge Q is placed at the centre of the spherical cavity. What will be the surface charge density on .
(i) the inner surface (ii) the outer surface?