

How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms :
(a) Hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing
(b) Crystal lattice and unit cell
(c) Tetrahedral void and octahedral void.
(a) In hexagonal close packing (hcp), the spheres of the third layer are vertically above the spheres of the first layer
(ABABAB……. type). On the other hand, in cubic close packing (ccp), the spheres of the fourth layer are present above the spheres of the first layer (ABCABC…..type).
(b) Crystal lattice: It deplicts the actual shape as well as size of the constituent particles in the crystal. It is therefore, called space lattice or crystal lattice.
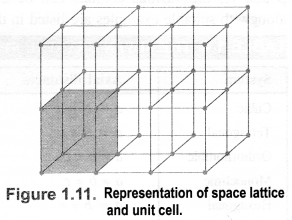 Unit cell: Each bricks represents the unit cell while the block is similar to the space or crystal lattice. Thus, a unit cell is the fundamental building block of the space lattice.
Unit cell: Each bricks represents the unit cell while the block is similar to the space or crystal lattice. Thus, a unit cell is the fundamental building block of the space lattice.
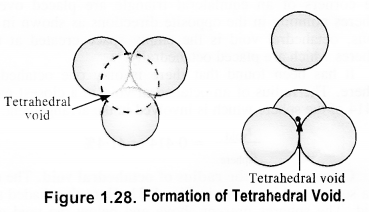
(c) Tetrahedral void: A tetrahedral void is formed when triangular void made by three spheres of a particular layer and touching each other.
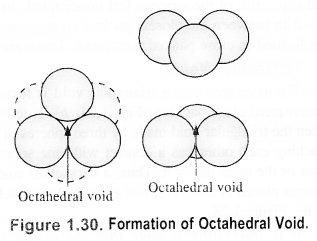
Octahedral void: An octahedral void or site is formed when three spheres arranged at the corners of an equilateral triangle are placed over anothet set of spheres.
A group 14 element is to be converted into n-type semiconductor by doping it with a suitable impurity. To which group should this impurity belong?
‘Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting points’. Comment. Collect melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane from a data book. What can you say about the intermolecular forces between these molecules?
Which of the following lattices has the highest packing efficiency (i) simple cubic (ii) body- centred cubic and (iii) hexagonal close-packed lattice?
Non-stoichiometric cuprous oxide, Cu2O can be prepared in laboratory. In this oxide, copper to oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2:1. Can you account for the fact that this substance is a p-type semiconductor?
Explain how vacancies are introduced in an ionic solid when a cation of higher valence is added as an impurity in it.
Gold (atomic radius = 0.144 nm) crystallises in a face centred unit cell. What is the length of the side of the unit cell ?
The total number of tetrahedral voids in the face centered unit cell is
(a) 6 (c) 10
(b) 8 (d) 12
In which of the following structure coordination number for cations and anions in the packed structure will be same?
(a) Cl– ions form fee lattice and Na+ ions occupy all octahedral voids of the unit cell.
(b) Ca2+ ions form fee lattice and F- ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell
(c) O2- ions form fee lattice and Na+ ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell
(d) S2- ions form fee lattice and Zn2+ ions go into alternate tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
Explain how many portions of an atom located at
(i)corner and (ii)body centre of a cubic unit cell is part of its neighbouring unit cell.
Classify the following as amorphous or crystalline solids: Polyurethane, naphthalene, benzoic acid, Teflon, potassium nitrate, cellophane, polyvinyl chloride, fibreglass, copper
Solid A is a very hard electrical insulator in. solid as well as in molten state and melts at extremely high temperature. What type of solid is it?
A compound forms hexagonal close-packed. structure. What is the total number of voids in 0. 5 mol of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
Copper crystallises into a fee lattice with edge length 3.61 x 10-8 cm. Show that the calculated density is in agreement with its measured value of 8.92 gcm-3.
A sample of ferrous oxide has actual formula Fe0.93 O1.00. In this sample, what fraction of metal ions are Fe2+ ions? What is the type of non-stoichiometric defect present in this sample? '
What is the two-dimensional coordination number of a molecule in square close-packed layer?
Ionic solids, which have anionic vacancies due to metal excess defect, develop colour. Explain with the help of a suitable example.
What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be converted into glass?
(i) What is meant by the term coordination number’?
(ii) What is the coordination number of atom
(a) in a cubic close-packed structure?
(b) in a body centred cubic structure?
How many lattice points are there is one unit cell of each of the following lattices?
(i) Face centred cubic (if) Face centred tetragonal (iii) Body centred cubic
If the radius of the octahedral void is r and radius of the atoms in close-packing is R, derive relation between rand R.
Which of the following is not the characteristic of ionic solids?
(a) Very low value of electrical conductivity in the molten state
(b) Brittle nature
(c) Very strong forces of interactions
(d) Anisotropic nature
Which of the following defects decrease the density?
(a) Interstitial defect (b) Vacancy defect
(c) Frenkel defect (d) Schottky defect
Distinguish between :
(i) Hexagonal and monoclinic unit cells
(ii) Face-centred and end-centred unit cells.
What is the two-dimensional coordination number of a molecule in a square close-packed layer?
Ionic solids, which have anionic vacancies due to metal excess defect, develop colour. Explain with the help of a suitable example.
In terms of band theory, what is the difference
Explain the following with suitable example:
Classify .the following solids in different categories based on the nature of intermolecular forces operating in them: Potassium sulphate, tin, benzene, urea, ammonia, water, zinc sulphide, graphite, rubidium, argon, silicon carbide
Distinguish between
(i) Hexagonal and monoclinic unit cells
(ii) Face-centred and end-centred unit cells.
A group 14 element is to be converted into n-type semiconductor by doping it with a suitable impurity. To which group should this impurity belong?
How can you determine the atomic mass of an unknown metal if you know its density and the dimensions of its unit cell? Explain.
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for (i) simple cubic, (ii) body centred cubic, and (iii) face centred cubic (with the assumptions that atoms are touching each other).
What is the coordination number in a square close packed structure in two dimensions? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6
Which of the following statements are not true?
(a) Vacancy defect results in a decrease in the density of the substance
(b) Interstitial defects results in an increase in the density of the substance
(c) Impurity defect has no effect on the density of the substance
(d) Frenkel defect results in an increase in the density of the substance
Under the influence of electric field, which of the following statements are true about the movement of electrons and holes in a p-type semiconductor?
(a) Electron will move towards the positively charged plate through electron holes
(b) Holes will appear to be moving towards the negatively charged plate
(c) Both electrons and holes appear to move towards the positively charged plate
(d) Movement of electrons is not related to the movement of holes
The number of tetrahedral voids per unit cell in NaCl crystal is
(c) twice the number of octahedral voids
(d) four times the number of octahedral voids
Which of the following features are not shown by quartz glass?
(a) This is a crystalline solid
(b) Refractive index is same in all the directions
(c) This has definite heat of fusion
(d) This is also called super cooled liquid
A compound is formed by two elements M and N. The element N forms ccp and atoms of the element M occupy 1/3 of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound? (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2015)
Niobium crystallises in a body centred cubic structure. If density is 8.55 g cm-3, calculate atomic radius of niobium, using its atomic mass 93u.
Refractive index of a solid is observed to have the same value along all directions. Comment on the nature of this solid. Would it show cleavage property?