

Justify that the following reactions are redox reactions:
(a) CuO(s) + H2(g) —–> Cu(s) + H20(g)
(b) Fe2O3(s) +3CO(g) —-> 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
(c) 4BCl3(g) +3LiAlH4(s) ——> 2B2H6(g) + 3LiCl(s) + 3AlCl3(s)
(d) 2K(s) +F2(g)——> 2K+F–(s)
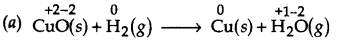
Here, O is removed from CuO, therefore, it is reduced to Cu while O is added to H2 to form H20, therefore, it is oxidised. Further, O.N. of Cu decreases from + 2 in CuO to 0 in Cu but that of H increases from 0 in H2 to +1 in H20. Therefore, CuO is reduced to Cu but H2 is oxidised to H20. Thus, this is a redox reaction.
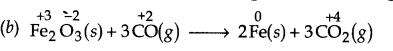
Here O.N. of Fe decreases from +3 if Fe2O3 to 0 in Fe while that of C increases from +2 in CO to +4 in CO2. Further, oxygen is removed from Fe2O3 and added to CO, therefore, Fe2O3 is reduced while CO is oxidised. Thus, this is a redox reaction.
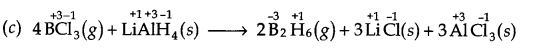
Here, O.N. of B decreases from +3 in BrCl3to -3 in B2H6 while that of H increases from -1 in LiAlH4to +1 in B2H6. Therefore, BCl3 is reduced while LiAlH4 is oxidised. Further, H is added to BCl3 but is removed from LiAlH4, therefore, BC13 is reduced while LiAlH4 is oxidised. Thus, it is a redox reaction.
Here, each K atom as lost one electron to form K+ while F2 has gained two electrons to form two F– ions. Therefore, K is oxidised while F2 is reduced. Thus, it is a redox reaction.
By chemical bonding, C2 is attached to three H-atoms (less electronegative than carbon) and one CH2OH group (more electronegative than carbon), therefore,
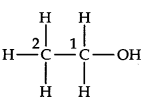
O.N. of C2 = 3 (+1) + x + 1 (-1) = 0 or x = -2 C2 is, however, attached to one OH (O.N. = -1) and one CH3 (O.N. = +1) group, therefore, O.N. of C4 = + 1 + 2 (+1) + x + 1 (-1) = 0 or x = -2
Identify the correct statements with reference to the given reaction.
P4 + 30H– + 3H20→ PH3 + 3H2 P0–2
(a) Phosphorus is undergoing reduction only.
(b) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation only.
(c) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation as well as reduction.
(d) Hydrogen is undergoing neither oxidation nor reduction
Calculate the oxidation number of phosphorus in the following species.
(a) HPO32- and (b) P043-
While sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide can act as an oxidising as well as reducing agents in their reactions, ozone and nitric acid act only as oxidants. Why?
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric add, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum wight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.0 g of ammonia and 20.0 g of oxygen?
Arrange the following metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts.Al, Cu, Fe, Mg and Zn.
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the folloxving:
(i) An aqueous solution of AgNO3 with silver electrodes.
(ii) An aqueous solution of silver nitrate with platinum electrodes.
(iii) A dilute solution of H2S04with platinum electrodes.
(iv) An aqueous solution of CuCl2 with platinum electrodes.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are not true about the following decomposition reaction?
2KCIO3 →2KC1 + 302
(a) Potassium is undergoing oxidation.
(b) Chlorine is undergoing oxidation.
(c) Oxygen is reduced.
(d) None of the species are undergoing oxidation or reduction.
Justify-giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxidant and among hydrohalic compounds, hydroiodic add is the best reductant.
Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
(a) A13-/A1; E °= -1.66 V
(b) Fe2+ /Fe; E °= -0.44 V
(c) Cu2+/ Cu E °=34 V
(d) F2(g)/2F–(aq) E °= 2.87 V
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction, Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) ————> Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
takes place. Further show:
(i) which of the electrode is negatively charged.
(ii) the carriers of current in the cell and
(iii) individual reaction at each electrode.
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in them

Write Jour informations about the reaction:
(CN)2(g) + 2OH–(aq) —–> CN–(aq) + CNO–(aq) + H2O(l)
Which of the following elements does not show disproportionation tendency?
(a) Cl
(b) Br
(c) F
(d) I
(a) Balance the following equation by oxidation number method or by ion electron (half reaction) method.
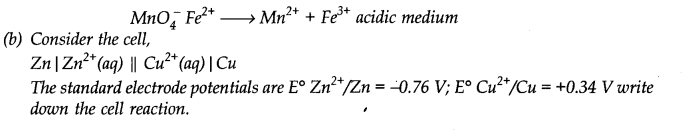
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
(i) Fe2+ + H+ + Cr2072- →Cr3+ + Fe3+ + H20
(ii) I2 + N0–3→ N02 +I03
(iii) I2 + S2032- →I– + S4062- ‘
(iv) MnO, + C2042-→ Mn2+ + CO2
Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing agent for each of the following reactions.
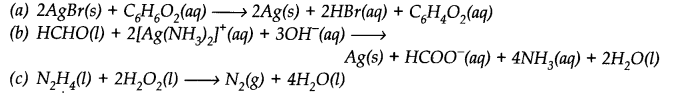
Identify disproportionation reaction
(a) CH4 + 202 → C02 + 2H20
(b) CH4 + 4C12 → CC14 + 4HCl
(c) 2F2 + 20H–→2F– + OF2 + H20
(d) 2N02 + 20H– → N02 + NO–3 + H20
The reaction Cl2(g) + 20H–(aq)→ Cl0–(aq) + Cl–(aq) + H20(l) represents the process of bleaching. Identify and name the species that bleaches the substances due to its oxidizing action.
Calculate the oxidation number of each sulphur atom in the following compounds:
(a) Na2S203
(b) Na2S406
(c) Na2S03
(d) Na2S04
Fluorine reacts with ice and results in the change:
H20(S) + F2 (g) ——-> HF(g) + HOF(g)
Justify that this reaction is a redox reaction.
Consider the reactions:

Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react difforerently with iodine and bromine?
Identify the correct statement(s) in relation to the following reaction:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
(a) Zinc is acting as an oxidant.
(b) Chlorine is acting as a reductant.
(c) Hydrogen ion is acting as an oxidant.
(d) Zinc is acting as a reductant.

Write formulas for the following compounds:
(a) Mercury (II) chloride, (b) Nickel (II) sulphate, (c) Tin (IV) oxide, (d) Thallium
(I) sulphate, (e) Iron (III) sulphate, (f) Chromium (III) oxide.
Mn02-4 undergoes disproportionation reaction in acidic medium but Mn0–4 does not. Give reason.
The compound AgF2 is unstable. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why?
What is meant by electrochemical series? What are characteristics of electrochemical series?
Write the O.N of all the atoms for the following well known oxidants?
(i) KMnO4 (ii) K2Cr2O7 (iii) KClO4
Identify the oxidant and the reductant in the following reaction.
N2H4(g) + ClO4(aq) ———–> NO(g) + Cr(aq)
In which of the following compounds, an element exhibits two different oxidation states.
(a) NH2OH
(b) NH4NO3
(c) N2H4
(d) N3H
The exhibition of various oxidation states by an element is also related to the outer orbital electronic configuration of its atom. Atom(s) having which of the following outermost electronic configurations will exhibit more than one oxidation state in its/their compounds.
(a) 3s1
(b) 3dl4s2
(c) 3d24s2
(d) 3s23p3
Refer to the periodic table given in your book and now answer the following questions.
(a) Select the possible non-metals that can show disproportionation reaction.
(b) Select three metals that show disproportionation reaction.
Thiosulphate reacts differently with iodine and bromine in the reactions given below:
2S2032_ + I2→S4062- + 2I–
S2032- + 2Br2 + 5H20 →2S042- + 4Br– + 10H+
Which of the following statements justifies the above dual behaviour of thiosulphate?
(a) Bromine is a stronger oxidant than iodine.
(b) Bromine is a weaker oxidant than iodine.
(c) Thiosulphate undergoes oxidation by bromine and reduction by iodine in these reactions.
(d) Bromine undergoes oxidation and iodine undergoes reduction in these reactions.
Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent and reacts with PbO but it does not react with Pb02. Explain why?
Suggest a list of substances where carbon can exhibit oxidation states from -4 to +4 and nitrogen from -3 to +5.