Question:
The Earth attracts an apple. Does the apple also attract the Earth? If it does, why does the Earth not move towards the apple?
Answer:
According to Newton's law of gravitation, both apple and the earth attract each other with equal force but in opposite directions. Also they they produce different accelerations depending on the mass of the object. It means apple also attract the Earth. Since the mass of the earth is extremely large as compared to mass of the apple, acceleration of the earth due to this force of attraction is very low (of order 10
-25 m/s
2).
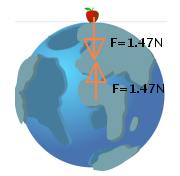
Mathematically, mass of an apple (m
apple) = 150g = 0.15 kg
mass of the earth (m
E) = 6 × 10
24 kg
acceleration acting on apple due to gravity (g) of earth = 9.8 m/s
2 Weight of the apple = m
apple× g = 0.15 × 9.8 = 1.47 N
⇒ Earth also experiences 1.47 N force.
i.e. m
E × a = 1.47N
a = 1.47 / 6 × 10
24= 2.45 × 10
-25 m/s
2 (extremely small value)
Gravitation
Q 1.
State Kepler’s Laws of planetary motion. How did Newton guess inverse square law ?
Q 2.
Calculate the force of gravitation between the Earth and the Sun,given that the mass of the Earth =
kg and mass of the Sun =
kg. The average distance between the two is
m.
Q 3.
Can you calculate density of Earth from Newton’s law of gravitation ?
Q 4.
What do we call the gravitational force between the Earth and an object ?
Q 5.
What is the value of ‘g’ at the centre of Earth ?
Q 6.
What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity ?
Q 7.
At what height above the surface of the earth, the value of 'g' becomes 64% of its value at the surface of the earth. Take radius of the earth = 6400 km.
Q 8.
A particle is dropped from a tower 180 m high.How long does it take to reach the ground ? What is the velocity when it touches the ground ? Take g =
Q 9.
Fill in the blanks :
Weight of an object is the product of ______ and ________.
Q 10.
Why do sewing needles and all pins have a sharp pointed tip?
Q 11.
Suppose a planet exists whose mass and radius both,are half those of Earth.Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of this planet.
Q 12.
Fill in the blanks :
Every object in the universe ________ other bodies.
Q 13.
Two stones A and B are dropped from a multistoried building. A is dropped from 100 m and after some time B is dropped from 50 m height. Both of them reach the earth at the same time. Will they have equal velocity while reaching the ground ? Calculate and find out the answer (take g =10 m/s
2).
Q 14.
Calculate the value of acceleration due to gravity on Moon. Given mass of Moon =
kg, radius of Moon = 1740 km
Q 15.
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 10
24 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 10
30 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 10
11 m.
Q 16.
Is weight a scalar quantity?
Q 17.
A boy on a clif£ 49 m high drops a stone.One second later,he throws a second stone after the first.They both hit the ground at the same time. With what speed did he throw the second stone ?
Q 18.
In Fig.,the line that joins a planet to the sun sweeps out areas
,
in time intervals 6 weeks,3 weeks and 2 weeks respectively.How are
,
realted ?

Q 19.
Fill in the blanks :
The gravitational force between the earth and the object is generally called ____________.
Q 20.
The distance between two objects is doubled. What happens to gravitational force between them
Q 21.
Can a body have mass but no weight ?
Q 22.
Compare gravitational force between light objects and heavy objects.
Q 23.
What are the Kepler Laws that govern the motion of the planets?
Q 24.
Who measured the value of G first time, experimentally?
Q 25.
Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Q 26.
Mass of an object is 10 kg. What is its weight on the Earth? (g = 9.8 m/s
2.)
Q 28.
Fill in the blanks :
A body is said to be in _______ when only gravity acts on it.
Q 29.
Fill in the blanks :
________ of an object is the force of gravity acting on it.
Q 30.
Fill in the blanks :
The SI unit of mass is ______.
Q 31.
Fill in the blanks :
It is the ____________ of the earth, which holds our atmosphere in place.
Q 32.
Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of the water?
Q 33.
In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
Q 34.
The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm
3. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is 1 g cm
-3? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Q 35.
Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Q 36.
What is the gravitational acceleration of a spaceship at a distance equal to two Earth’s radius from the centre of the Earth ?
Q 37.
A stone drops from the edge of the roof.It passes a window 2 m high in 0.1 s.How far is the roof above the top of the window
Q 38.
What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight ?
Q 39.
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the Earth and a 1 kg on its surface ? (Mass of the Earth Is
kg and radius of the Earth is
m.)
Q 40.
Who explained the motion of planets around the Sun ?
Q 41.
Can a body have weight but no mass ?
Q 42.
Define g and G.Establish relation between them.
Q 43.
On earth,value of G =
.What is its value on moon,where g is nearly
th that of earth ?
Q 44.
Fill in the blanks :
Heliocentric model was proposed by ______.
Q 45.
Fill in the blanks :
The value of Universal Gravitation constant (G) is ________ Nm
2kgs
-2.
Q 46.
Fill in the blanks :
The value of
g on the earth's surface is ______.
Q 47.
Fill in the blanks :
The SI unit of weight is _____.
Q 48.
What was heliocentric theory? Who proposed this?
Q 49.
State the universal law of gravitation.
Q 50.
Why is G called the Universal Constant?



