

What is meant by ‘demineralised water’ and how can it be obtained?
Demineralised water is free from all soluble mineral salts which is obtained by passing water successively through a cation exchange (in the form of H+) and an anion exchange in the form of OH– resins.
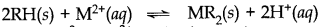
H+ exchanges for Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and other cations present in water. This process results in release of proton which makes the water acidic.
OH– exchanges, for anions like Cl–, HCO3–,SO42-etc.
OH– ions thus liberated neutralize the H+ ions set free in the cation exchange process. H+(aq) + OH–(aq) ——-> H2O(l)
Do you expect different products in solution when aluminium (III) chloride and potassium chloride treated separately with (i) normal water (ii) acidified water (iii) alkaline water? Write equation wherever necessary.
Justify the position of hydrogen in the periodic table on the basis of its electronic configuration.
Dihydrogen reacts with dioxygen (02) to form water. Write the name and formula of the product when the isotope of hydrogen which has one proton and one neutron in its nucleus is treated with oxygen. Will the reactivity of both the isotopes be the same towards oxygen? Justify your answer.
Why does H+ ion always get associated with other atoms or molecules?
(a) Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals.
(b) Its reactivity is similar to halogens.
(c) It resembles both alkali metals and halogens.
(d) Loss of an electron from hydrogen atom results in a nucleus of very small size as compared to other atoms or ions. Due to small size it can not exist freely.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct in the case of heavy water?
(a) Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactor.
(b) Heavy water is more effective as solvent than ordinary water.
(c) Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water.
(d) Heavy water has lower boiling point than ordinary water.
(a) How is dihydrogen prepared from water by using a reducing agent?
(b) Give the industrial use of dihydrogen which depends upon heat liberated when it bums.
Which of the following reactions increases production of dihydrogen from synthesis gas?

Saline hydrides are known to react with water violently producing fire. Can C02, a well known fire extinguisher, be used in this case? Explain.
Why does hydrogen occur in a diatomic form rather than in a monoatomic form under normal conditions?
Hydrogen peroxide is obtained by‘the electrolysis of _______.
(a) water
(b) sulphuric acid
(c) hydrochloric acid
(d) fused sodium peroxide
Write chemical reactions to justify that hydrogen peroxide can function as an oxidising as well as reducing agent.
What do you understand by the term ‘auto-protolysis of water? What is its significance?
Among NH3 H2O and HE, which would you expect to have highest magnitude of hydrogen bonding and why?
Complete the following chemical reactions.
(i) PbS(s) + H2O2 (aq) ————->
(ii) MnO4– (aq) + H2O2 (aq) ————->
(iii) CaO(s) + H2O(g) ————->
(iv) AlCl3(g) + H2O(l)————->
(v) Ca3N2(S) + H2O(l) ————->
Classify the above into (a) hydrolysis, (b) redox and (c) hydration reactions.
Discuss the principle and method of softening of hard water by synthetic ion-exchange resins.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Metallic hydrides are deficient of hydrogen.
(b) Metallic hydrides conduct heat and electricity.
(c) Ionic hydrides do not conduct electricity in solid state.
(d) Ionic hydrides are very good conductors of electricity in solid state.
Discuss the consequences of high enthalpy of H-H bond, in terms of chemical reactivity of dihydrogen.
Is demineralised or distilled water useful for drinking purposes? If not, how can it be made useful ?
Explain the following:
(i) Temporary hardness can remove by boiling
(ii) Soft water lathers with soap but hard water not.
(i)Draw the gas phase and solid phase structure of H202.
(ii) H202 is a better oxidizing agent than water. Explain.
What characteristics do you expect from an electron-deficient hydride with respect to its structure and chemical reaction?
Arrange the following:
(i) CaH2, BeH2 and TiH2 in order of increasing electrical conductance.
(ii) LiH, NaH and CsH in order of increasing ionic character.
(iii) H-H, D—D and F—F in order of increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(iv) NaH, MgH2 and H2O in order of increasing reducing property.
What do you understand by the term ‘auto-protolysis’ of water? what is its significance?
Consider the reaction of water with F2 and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidised/reduced ?
Which gas is evolved when Mg3N2 (Magnesium nitride) is treated with H2O? Give chemical reaction.
Which of the following hydrides is electron-precise hydride?
(a) B2H6
(b) NH3
(c) H20
(d) CH4
Which of the following equatibns depicts the oxidizing nature of H202?
(a) 2Mn0–4 + 6H+ + 5H202 → 2Mn2+ + 8H20 + 502
(b) 2Fe3+ + 2H+ + H202 → 2Fe2+ + 2H20 + 02
(c) 2I– + 2H+ + H202 → I2 + 2H20
(d) KI04 + H202 → KI03 + H20 + 02
Which of the following statements are not true for hydrogen?
(a) It exists as diatomic molecule.
(b) It has one electron in the outermost shell.
(c) It can lose an electron to form a cation which can freely exist.
(d) It forms a large number of ionic compounds by losing an electron.
Dihydrogen can be prepared on commercial scale by different methods. In its preparation by the action of steam on hydrocarbons, a mixture of CO and H2 gas is formed. It is known as _____ .
(a)water gas
(b) syn gas
(c) producer gas
(d) industrial gas